MODULE 1: SQL INJECTION
Module Objectives
- Understanding SQL injection concepts
- Understanding Various Types of SQL injection attacks
- Understanding SQL injection Methodology
- Understanding Various SQL injection tools
- Understanding different IDS evasion techniques
- Adopting SQL injection Countermeasures
- Overview of Various SQL injection Detection Tools
What is SQL injection
- (SQL)structured query language is a textural language used by a database server. SQL injection is a technique where attackers take advantage of un sanitized input vulnerabilities, to pass commands through a web application or a database server.
- SQL commands used to perform operations on the database include INSERT ,SELECT, UPDATE and DELETE. These commands are used to manipulate data in the database server.
- In a SQL injection, an attacker injects the malicious SQL queries into the user INPUT form either to gain access to a database or to retrieve information directly from the database.
Such attacks are possible because of flaws in web applications and not because of any issues with the database or web server
Why bother about SQL injection?
- SQL injection can be used to implement the following
1. Authentication bypass - an attacker alters authorization information stored in the database by exploiting an SQL injection vulnerability
2.Information Disclosure - an attacker obtains sensitive information that is stored in the database
3. Compromised Data Integrity - an attacker defaces a web page, inserts malicious content into web pages.
4.Compromised Availability of Data - an attacker deletes the database information content into web pages, or alters the contents of the database.
5.Remote Code Execution - an attacker compromises the Host OS(operating system)
UNDERSTANDING A HTTP POST REQUEST
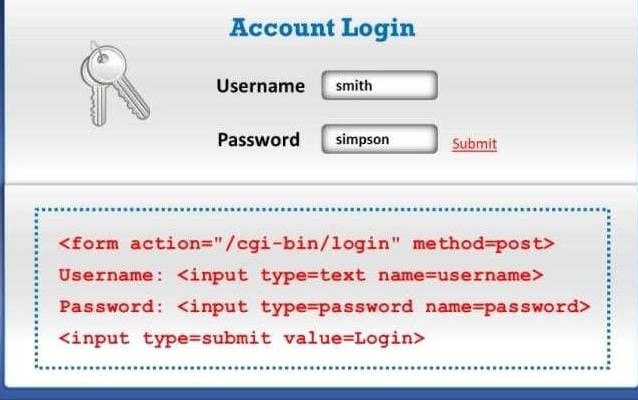
A HTTP POST request is a method for carrying the requested data to the web server. The HTTP POST request carries the requested data as part of the message body, Thus more secure than the HTTPS GET request.
UNDERSTANDING A NORMAL SQL QUERY
SQL queries include selecting data, retrieving data, inserting/updating data, and creating data objects such as databases and tables. Query statements begin with a command such as SELECT, UPDATE, CREATE, or DELETE. The diagram below shows a typical S0l query. It is constructed with user-supplied values, and uроn execution, it displays results from the database.
UNDERSTANDING AN SQL INJECTION QUERY
An SQL injection query exploits the normal execution of SQL. An attacker submits a request, with values that will execute normally but return data from the database that the attacker seeks.
The attacker can submit these malicious values because of the inability of the application to filter them before processing
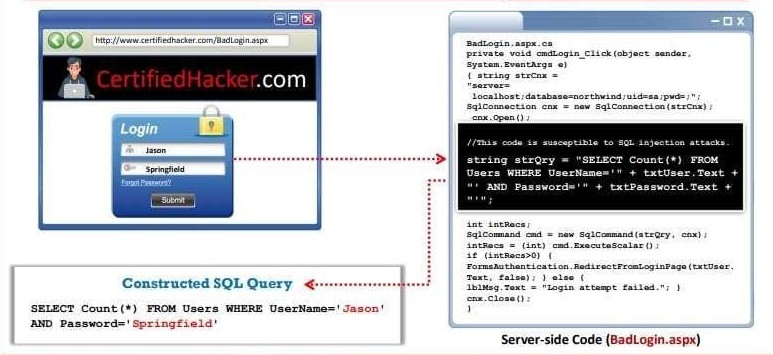
An HTML form that receives and passes information posted by the user to the Active Server Pages(ASP) script running on an IlS web server is the best example of SQL injection. The information passed is the username and password. To create an SQL injection query, an attacker may submit the following values in application input fields, such as the username and password fields.
Username: Blah' or 1=1 --
Password: Springfield
As part of the normal execution of the query, these input values will replace placeholders, and
the query will appear as follows: SELECT Count(*) FROM Users WHERE Username='Blah' or 1=1 --' AND Password='Springfield';
An example of SQL injection attack
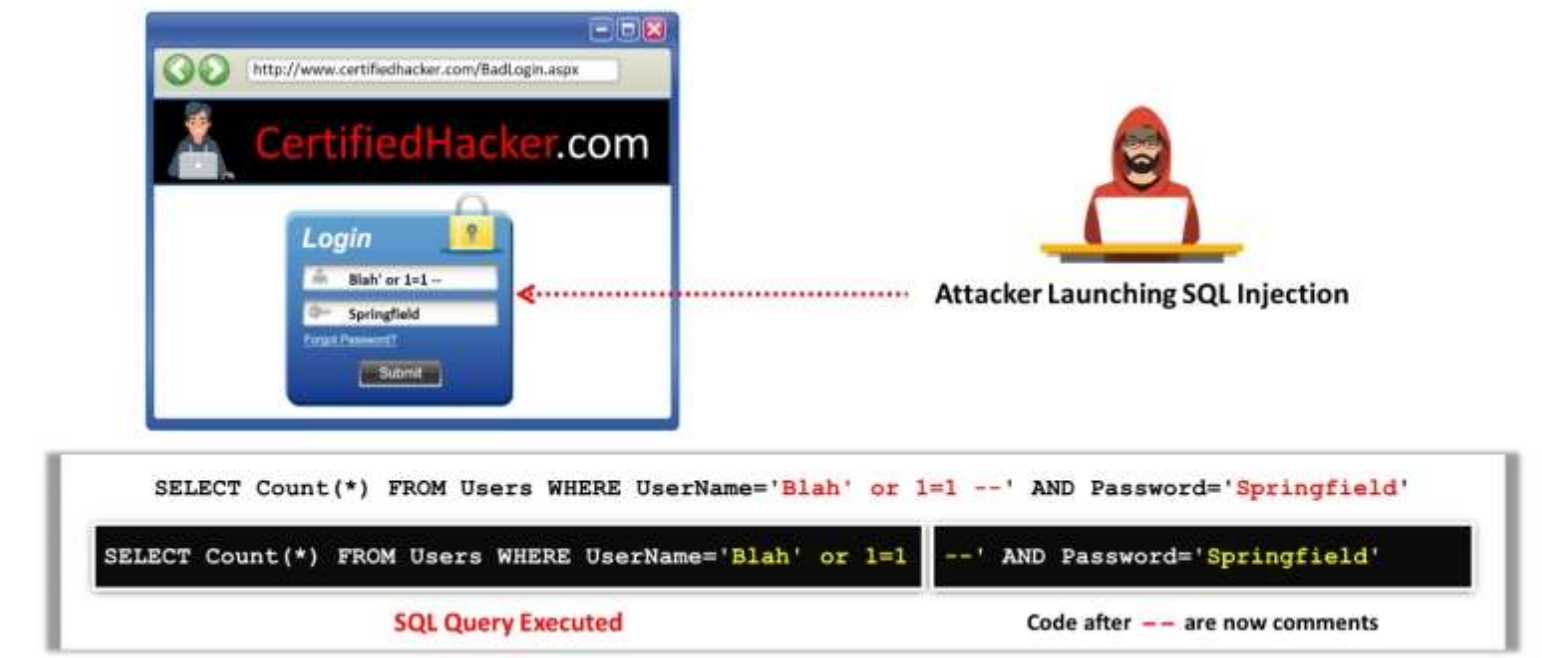
Understanding an SQL Injection Query—Code Analysis
Code analysis or code review is the most effective technique for identifying vulnerabilities or flaws in the code. An attacker exploits the vulnerabilities found in the code to gain access to the database. An attacker logs into an account by the following process:
- A user enters a username and password that match a record in the user's table
- A dynamically generated SQL query is used to retrieve the number of matching rows
- The user is then authenticated and redirected to the requested page
- When the attacker enters blah' or 1=1 --, then the SQL query will look like SELECT Count(*) FROM Users WHERE Username='blah' Or 1=1 --'AND Password=''
- A pair of hyphens indicate the beginning of a comment in SQL; therefore, the query simply becomes
SELECT Count(*) FROM Users WHERE Username='blah'Or 1=1
txtUser.Text +"'AND Password='" + txtPassword.Text +"'"; string strQry ="SELECT Count(*) FROM Users WHERE UserName='
Example of a Web Application Vulnerable to SQL Injection: Attack Analysis
Most websites provide search to enable users to find a specific product or service quickly. A separate Search field is maintained on the website in an area that is easily viewable. As with any other input field, attackers target this field to perform SQL injection attacks. An attacker enters specific input values in the Search field to perform an SQL injection attack.
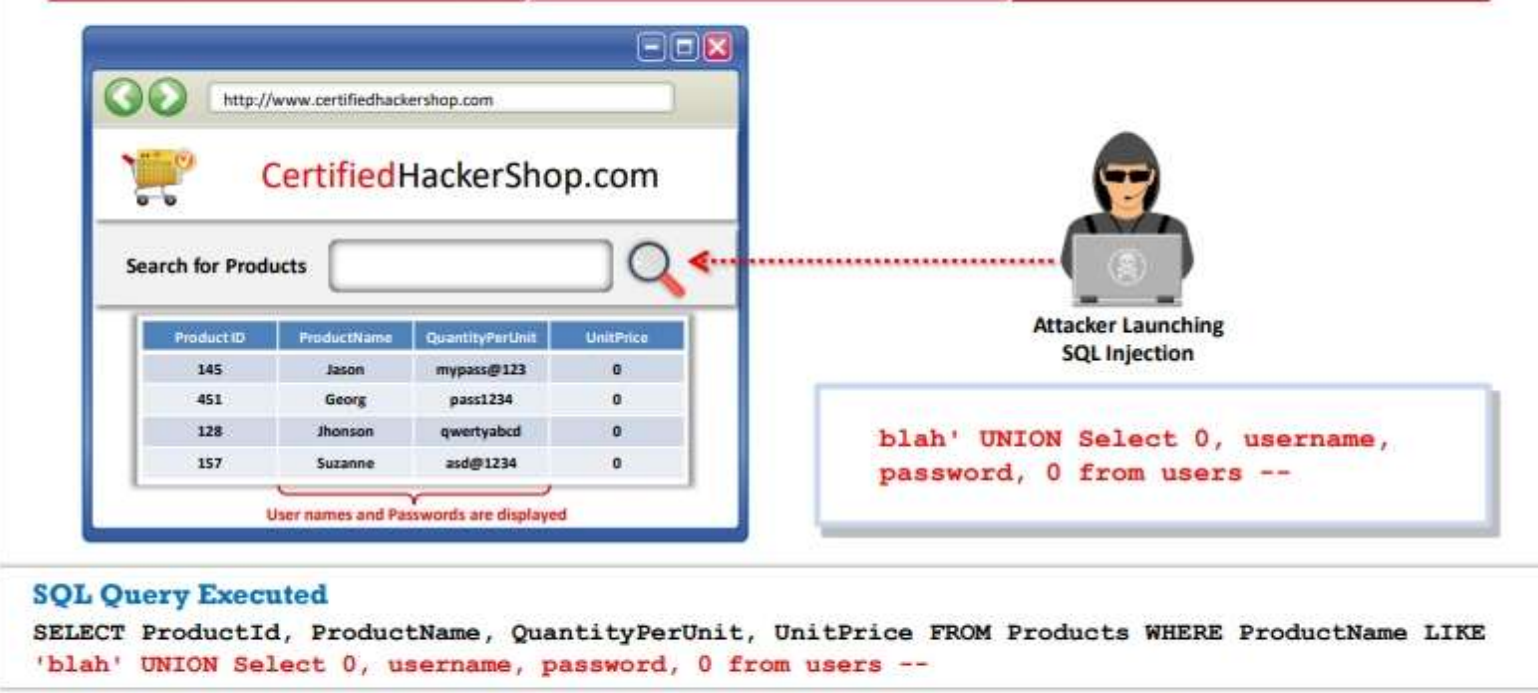
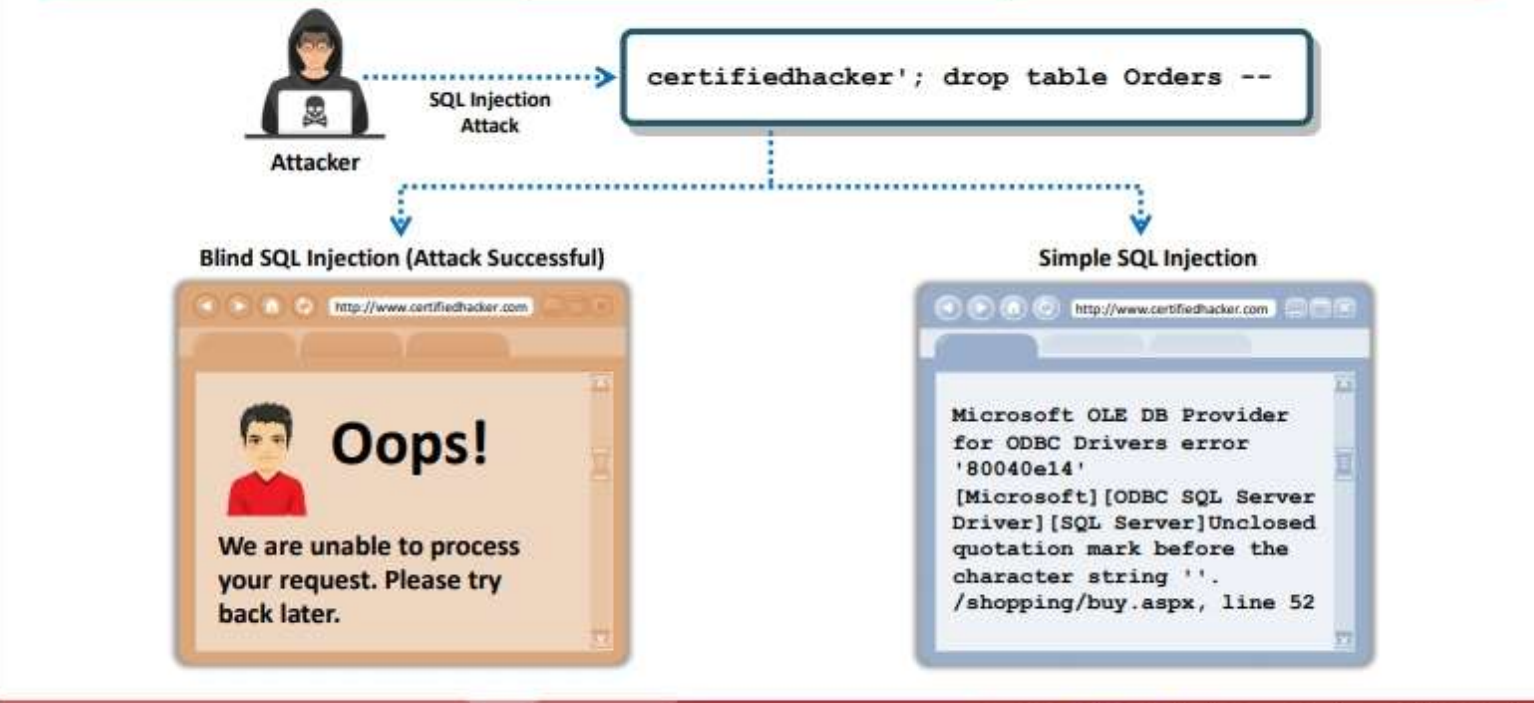
TYPES OF SQL INJECTION
In an SQL injection attack, the attacker injects malicious code through an SQL query that can read sensitive data and even can modify (insert/update/delete) it.
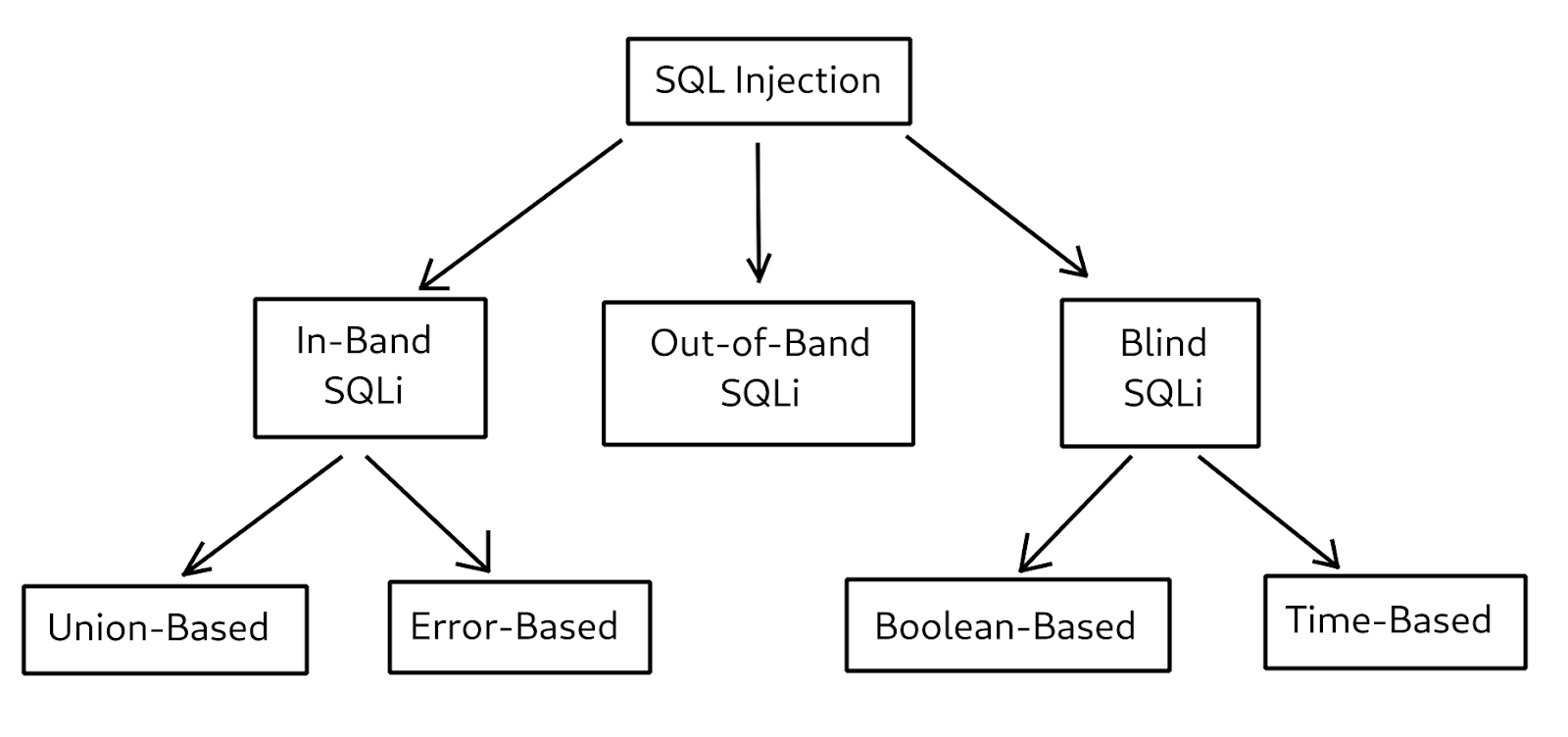
There are 3 main types of SQL injection;
1. In-band SQL Injection: An attacker uses the same communication channel to perform the attack and retrieve the results. In-band attacks are commonly used and easy-to exploit SQL injection attacks. The most commonly used in-band SQL injection attacks are error-based SQL injection and UNION SQL injection.
2. Blind/Inferential SQL Injection: In blind/inferential injection, the attacker has no error messages from the system to work on. Instead, the attacker simply sends a malicious SQL query to the database. This type of SQL injection takes a longer time to execute because the result returned is generally in Boolean form. Attackers use true or false results to determine the structure of the database and the data.
3.Out-of-Band SQL Injection: Attackers use different communication channels (such as database email functionality or file writing and loading functions) to perform the attack and obtain the results. This type of attack is difficult to perform because the attacker needs to communicate with the server and determine the features of the database server used by the web application.
1. IN BAND SQL injection
In in-band SQL injection, attackers use the same communication channel to perform the attack and retrieve the results. The most commonly used in-band SQL injection attacks are error-based SQL injection and UNION SQL injection.
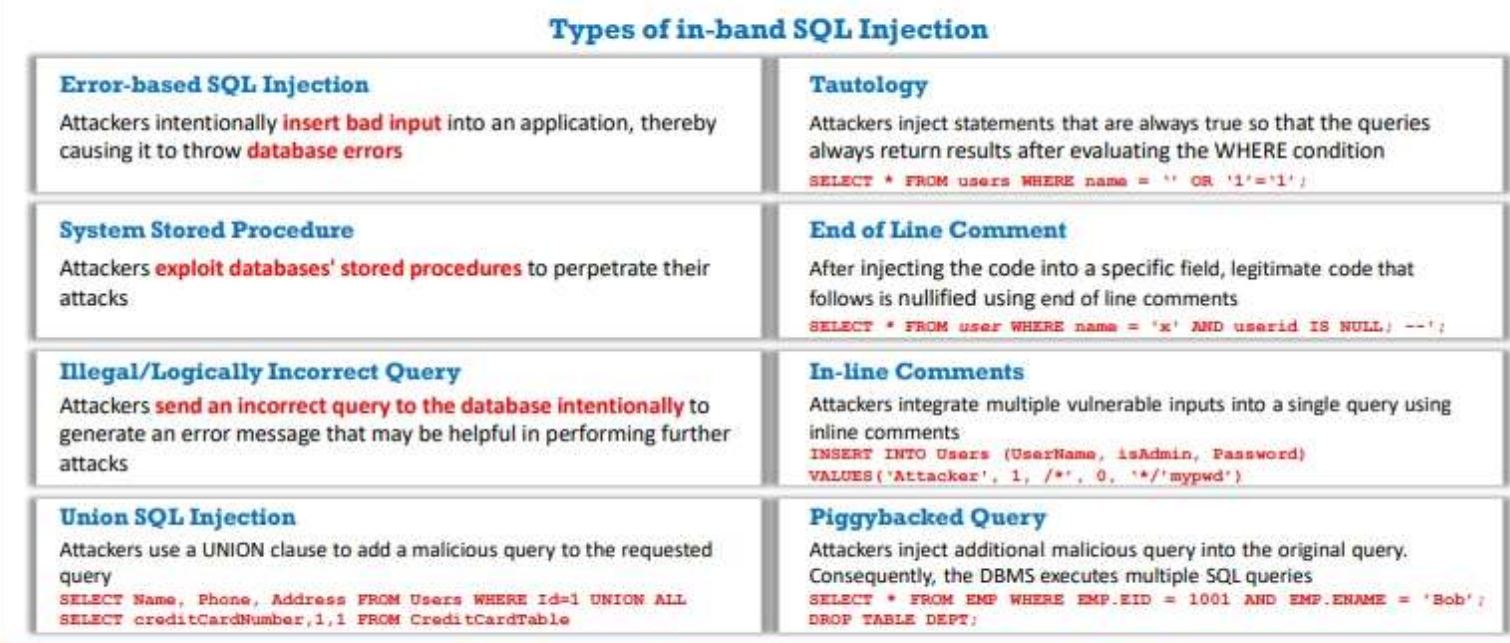
In a piggybacked SQL injection attack, an attacker injects an additional malicious query into the original query. This type of injection is generally performed on batched SQL queries. The original query remains unmodified, and the attacker's query is piggybacked on the original query
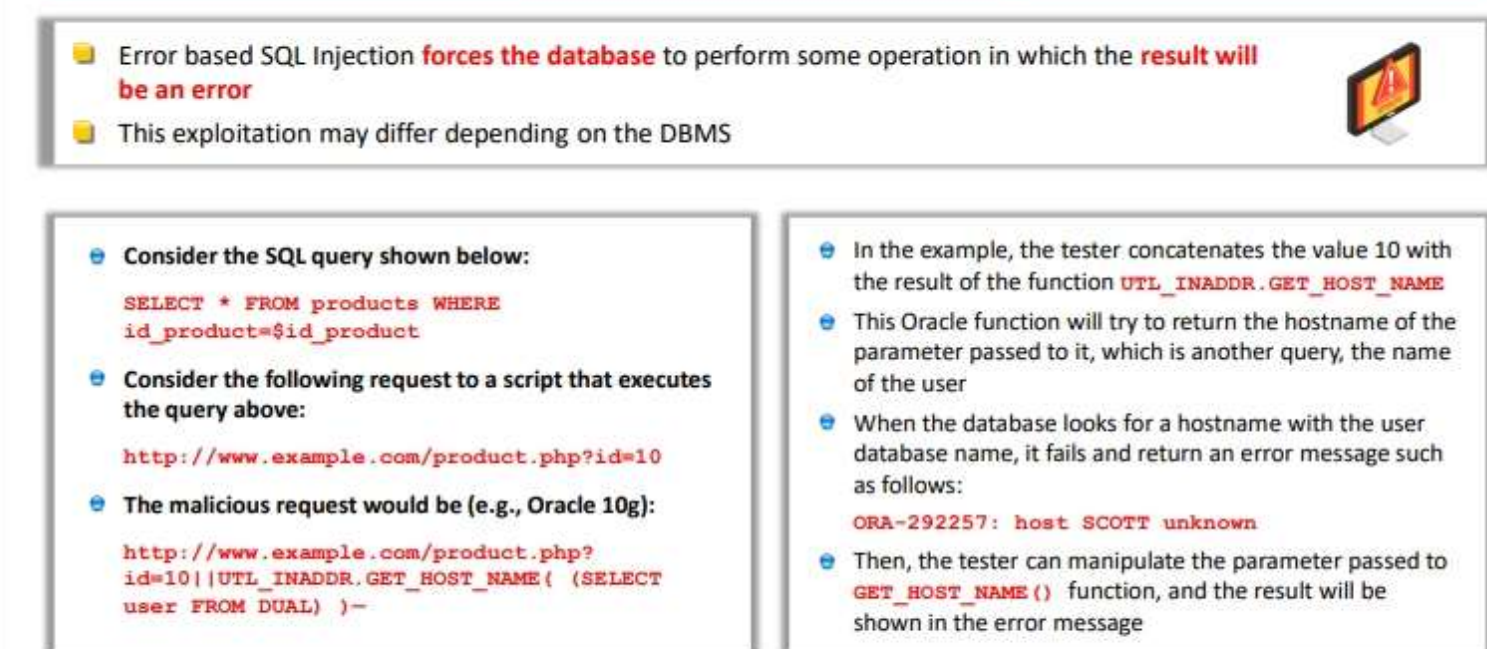
Error Based SQL Injection(under in band SQL)
in error-based SQL injection, the attacker forces the database to return error messages in response to his/her inputs. The attacker may analyse the error messages obtained from the underlying database to gather information that can be used for constructing the malicious query. The primary goal of this technique is to generate the error message from the database, which can be used to perform a successful SQL injection attack. Such exploitation may differ from one DBMS to another.
2.Blind/Inferential SQL Injection
Blind SQL Injection is used when a web application is vulnerable to an SQL injection but the results of the injection are not visible to the attacker. Blind SQL injection is identical to a normal SQL Injection except that when an attacker attempts to exploit an application, he/she sees a generic custom page instead of a useful error message. In blind SQL injection, an attacker poses a true or false question to the database to determine whether the application is vulnerable to SQL injection.
Blind injection differs from normal SQL in the manner of obtaining data from the database
No error message returned.